
Article 32 of the civil law, establishment and permission of non-profit corporations
The purpose of this institute is to establish theoretical systems of electromagnetic waves using technology, electromagnetic wave environments and associated industries through related research and studies. The institute will also pursue the development and distribution of the studies and the generalization of related theories in order to contribute to the improvement of mankind `s welfare and the development of the country.

1~2th Hyun-Bo Yoon

3thNak-Sam Jeong

4thHyuckjae Lee

5thDong Chul, Park

6thDong Il Kim

7thSeung In,Yang

8thNoh-Hoon Myung

9thSangwon Yun

10thYoung-Ki Cho

11th Jeong-Ki Pack

12thHai-Young Lee

13thYoung Joong Yoon

14thKi-Chai Kim

15thJaehoon Choi

16thTaek-Kyung Lee

17thKyung-Heon, Koo

18thSangwook Nam

19thChulhun Seo

20thBomson Lee

21thJeong-Hae Lee

22thKyeong-Sik Min

23thJin-Seob Kang

24thSeong-Ook Park

25thJong-Gwan Yook
| President | Choon Sik Cho | Korea Aerospace University | Professor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Executive Vice President | Jae-Sung Rieh | Korea University | Professor |
| Vice President | Chanho Kook | LIG Nex1 | Director |
| Vice President | Klaus Kim | SENSORVIEW | CEO |
| Vice President | Chan-Hong Kim | Agency for Defense Development | Center Director |
| Vice President | Taehoon Kim | Rohde & Schwarz Korea Limited | President |
| Vice President | Hyuk Park | Hanwha Systems | Executive Director |
| Vice President | Seung-Keun Park | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Director |
| Vice President | Young-Chul Park | Hankuk University of Foreign Studies | Professor |
| Vice President | Tak-Ki Ryu | ICT Technology Institute at SK Telecom | Director |
| Vice President | Jae Wook Lee | Korea Aerospace University | Professor |
| Vice President | Woorae Cho | Korea Aerospace Industries, LTD | Director |
| Executive Director | Kyung-Young Jung | Hanyang University | Professor |
| Director | Il-Suek Koh | Inha University | Professor |
| Director | Yong Bae Park | Ajou University | Professor |
| Director | Haejun Chung | Hanyang University | Professor |
| Executive Director | Hosung Choo | Hongik University | Professor |
| Director | Sungsik Wang | Hanyang Cyber University | Professor |
| Director | Jihoon Kim | Sejong Law Firm | Expert Committeeman |
| Director | Sungjoon Lim | Chung-Ang University | Professor |
| Executive Director | Moon-Que Lee | University of Seoul | Professor |
| Director | Young-Bae Jung | Hanbat National University | Professor |
| Director | Jungick Moon | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Director |
| Director | Choul-Young Kim | Chungnam National University | Professor |
| Director | Seunguk Ro | Kipco Aerospace & Defense Co,.LTD | Vice President |
| Executive Director | Yongshik Lee | Yonsei University | Professor |
| Director | Ic-Pyo HONG | Kongju National University | Professor |
| Director | JUNGHWAN HAN | Chungnam National University | Professor |
| Director | Kangwook Kim | Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Seung-Yeup Hyun | Jeju National University | Professor |
| Executive Director | Seungyoung Ahn | Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Woochan Lee | Incheon National University | Professor |
| Director | Hyunki Kim | LIG Nex1 | Head of Electronic Warfare Business Department |
| Director | Heesung Yoon | Sungwon Forming | President |
| Executive Director | Jung-Suek Oh | Seoul National University | Professor |
| Director | Sangjo Choi | Kyungpook National University | Professor |
| Director | Sanghoek Kim | Kyung Hee University | Professor |
| Director | Youngsu Kim | Comotech Corporation | President |
| Director | Sung-il Jung | mkor inc | Director |
| Director | Jaeyul Choo | Andong National University | Professor |
| Director | Tai-woong HA | Korea Radio Promotion Association | Team Leader |
| Executive Director | Youngwook Kim | Sogang University | Professor |
| Director | Ki Jin Han | Dongguk University | Professor |
| Director | Yong-Jae Kim | Smart Radar System Inc | Vice President |
| Director | GUN PYO JEON | Korea Communications Agency | Team Leader |
| Executive Director | Jong-Hwa Kwon | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Director |
| Director | EAKHWAN SONG | Kwangwoon University | Professor |
| Director | Il-Kyoo LEE | Kongju National University | Professor |
| Director | Hyun Ho Park | Suwon University | Professor |
| Director | Juno AN | Institute for Future Radio Engineering | CEO |
| Executive Director | Keum Cheol Hwang | Sungkyunkwan University | Professor |
| Director | JUN TEAG OH | Soongsil University | Professor |
| Director | Sung-Chan Song | Hanwha Systems | Director |
| Director | Byungkwan Kim | Chungnam National University | Professor |
| Executive Director | Jae-Young Chung | Seoul National University of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Junghoon Han | Korea Aerospace University | Professor |
| Director | Sung Jun Yang | Seoul National University of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Jae Hee Kim | Korea University of Technology & Education | Professor |
| Executive Director | Sanggeun Jeon | Korea University | Professor |
| Director | Jinho Jeong | Sogang University | Professor |
| Director | Jooyoung Jeon | Gangneung-Wonju National University | Professor |
| Director | Inchan Ju | Ajou University | Professor |
| Executive Director | Hyunchul Ku | Konkuk University | Professor |
| Director | Yeo-Sun Yoon | Sejong University | Professor |
| Director | Eunmi Choi | Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Sung Ho Wang | Nemesis | CEO |
| Executive Director | Dongho Kim | Sejong University | Professor |
| Director | EunHee KIM | Sejong University | Professor |
| Director | Jae-Gon Lee | Kyungnam University | Professor |
| Director | Seoneui Hong | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Principal Researcher |
| Executive Director | Ick-Jae Yoon | Chungnam National University | Professor |
| Director | Sangkil Kim | Pusan National University | Professor |
| Director | Young-Wan Kim | LIG Nex1 | Chief Researcher |
| Director | JoonYoung PARK | Hanwha Systems | Chief Researcher |
| Director | JISUNG PARK | ETNEWS | Journalist |
| Executive Director | Wang-Sang Lee | Gyeongsang National University | Professor |
| Director | Sun K. Hong | Soongsil University | Professor |
| Director | Dong-Wook Seo | Korea Maritime & Ocean University | Professor |
| Director | Myung Sun Song | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Principal Researcher |
| Executive Director | Wonbin Hong | Pohang University of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Wooyeol Choi | Seoul National University | Professor |
| Director | Byung Jang Jeong | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Principal Researcher |
| Executive Director | Byung-Wook Min | Yonsei University | Professor |
| Director | Jong-Ryul YANG | Konkuk University | Professor |
| Director | Ickhyun Song | Hanyang University | Professor |
| Director | Gangil Byun | Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology | Professor |
| Director | Jayil Ku | Korea Radio Promotion Association | Team Leader |
| Executive Director | Woojin Byun | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Center Director |
| Director | Han Lim Lee | Chung-Ang University | Professor |
| Director | Byunglae Cho | Agency for Defense Development | Team Leader |
| Director | Jong Pil Kim | LIG Nex1 | Director |
| Director | Hankil Jung | MOASOFT | Vice President |
| Auditor | Hyung-Do Choi | Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute | Director |
| Auditor | Jonghoon Kim | EMC Doctors Inc. | President |

Dear members of the Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science,
In an era when we cannot live even for a moment without electromagnetic waves (radio waves), we hope for year 2024 we will be able to overcome any difficulties and move forward with our members across generations and the world, with the infinite value of radio waves.
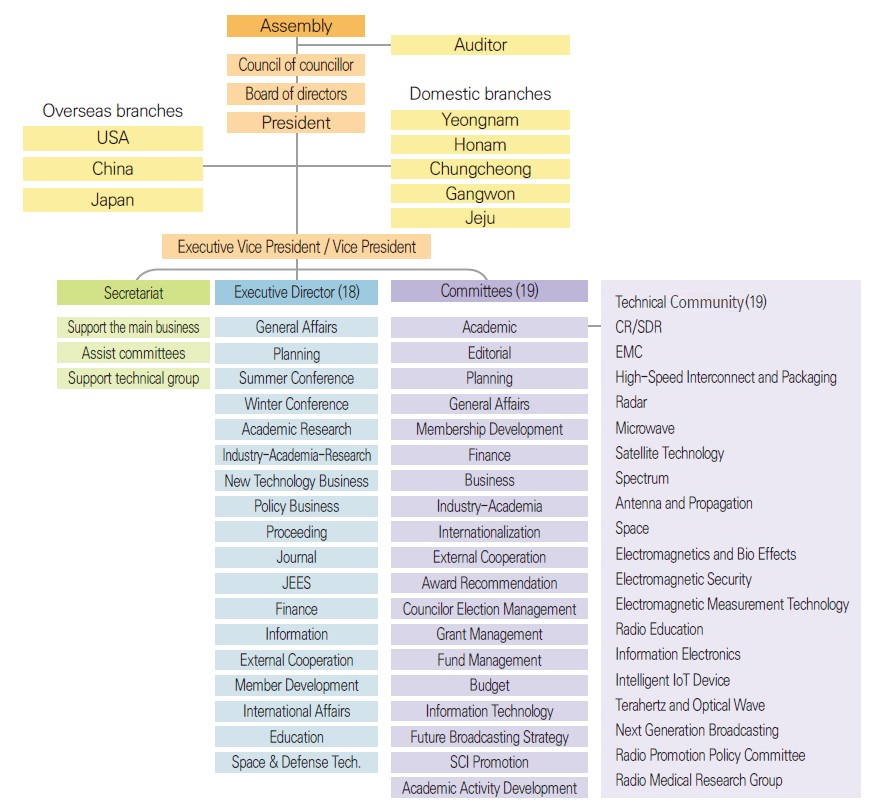
Founded in 1989, the Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science(KIEES) is a representative academic society in the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) field that celebrates its 35th anniversary this year. We pursue academic diversity while faithfully fulfilling its role in a socially responsible manner. In particular, we are publishing JKIEES(Journal of Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science), JEES(Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science) indexed in SCOPUS and SCIE, and KIEES magazine entitled “Electromagnetic Technology”. We are also actively conducting research and academic exchanges through branches in Chungcheong, Gyeongsang, Honam and Jeju in Korea, the United States, China, Japan, and more.
Keeping in mind the teachings of the Confucius' Analects of “和而不同,” which is to acknowledge differences, understand others, and achieve harmony, I would like to share the direction in which KIEES aims to take in 2024.
Firstly, KIEES will strive to support the growth and development of our members across generations. Recently, the number of new generations joining KIEES has increased significantly. We will give our full material and emotional support for the harmonious development of the current and future generations.
Secondly, KIEES aspires to move beyond the current world and reach broader and more distant places. Based on academic knowledge related to electromagnetic waves, we will support researchers to expand their expertise into new fields such as incorporation of quantum theory, leaping into satellites & space, convergence of digital radio, and medical care.
Thirdly, we will make every effort to establish ourselves as Korea’s IMS by upgrading the Winter and Summer Conferences to a comprehensive exhibition space and event for domestic radio waves-related organizations. We will do our best to promote mutual growth and development with radio wave-related companies.
Fourthly, we want to operate JKIEES and JEES(Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science) as systematically as possible. In the case of JKIEES, we will do our best to quickly and fairly review and publish valuable papers written in Korea by drastically shortenening the review period to 4 weeks for regular papers and 2 weeks for Letters. Accordingly, we will establish KIEES as an ideal academic society for presenting the research results of various members.
Fifthly, we will actively promote and revitalize international exchanges to raise KIEES's international status. In particular, we will conduct regular exchange programs with Asian countries such as China, which were temporarily suspended due to the COVID-19, and further strive to resume international academic conferences hosted by KIEES.
We will strive to inherit and build upon the great legacy across generations created by our senior members to become a proud KIEES. I believe there is no better space than this if we encourage and sympathize with each other in order to develop into the world's greatest academic society where we can interact with many people working in the field of electromagnetic waves and satisfy our academic curiosity. As the proud president of KIEES, I want to help each member become the best expert in his or her position and happily carry out academic research and exchanges.
We will strive to stand tall as an academic society that always reflects on the purpose of its establishment, seeks out new and adventurous research by exercising the intellectual curiosity which is the essence of an academic organizations, and actively interacts with researchers. I would like to ask our members to always join us so that we can study, research, exchange, share, and be happy together.
Thank you!
January 2024
President Choon Sik Cho
The Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science(KIEES)
| 1989. 6. 27. | The association of The Korea EMC/EMI Engineers was established. |
| 1989. 12. 30. | The Association of Korea EMC/EMI Engineers was approved by the MOIC(Ministry of Information and Communication). |
| 1989. 12. 30. | First Chairman(Lee, Joong Kun of Hanyang University) was elected. |
| 1990. 8. | First Chairman had resigned and New chairman(Yoon, Hyun Bo of Dongkook Univ.) was elected. |
| 1990. 11. 30. | Began to publish the Proceeding of EMI/EMC. |
| 1990. 12. 18. | The official name was changed from the Association of Korea EMC/EMI to The Korea EMI/EMC Society. |
| 1991. 11. 12. | First president (Yoon, Hyun Bo of Dongkook Univ.) was elected(Term : 92.1.-93.12.31). |
| 1992. 2. 21. | The Office moved to new building(Rm# 302, Dongkyo-dong, Mapo-ku Seoul). |
| 1993. 12. 11. | The proceeding was registered as a publication to the Ministry of Public Information. |
| 1993. 12. 11. | Second President(Yoon, Hyun Bo of Dongkook Univ.) was elected(Term : 94.1.-95.12.31). |
| 1995. 6. 3. | Renamed as "The Korea Electromagnetic Engineering Society(KEES)" from the previous name "The Korea EMI/EMC Society". |
| 1995. 7. 27. | Six Technical Groups were approved : Electromagnetic Environment, Spectrum Engineering, Microwave and Wave propagation, Electronic Materials and Components, Electromagnetic Wave Measurements, Electromagnetic Wave Application. |
| 1995. 10. 9. | The Office Moved to the current building. |
| 1996. 11. 20. | Youngnam and Honam branches were established. |
| 1995. 11. 25. | Third president(Chung, Nak Sam of KRISS) was elected(term : 96.1.-97.12.31). |
| 1996. 3. 29. | Technical Group of Electromagnetic Field and Biology was approved by Board of directors, and Committee of EMI/EMC Standards were named to Technical Group of EMI/EMC Standards. |
| 1996. 3. 31. | Separated the Journal from Proceeding(5 publications/year). |
| 1997. 1. 1. | Began to publish the Journal bimonthly and the Proceeding quarterly. |
| 1997. 11. 15. | Elected the fourth president(Lee, Hyuk Jae of ETRI) (Term : 98.1.-99.12.31). |
| 1997. 11. 27. | Became the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies. |
| 1998. 3. 4. | Became a member of the Korean Association of Academic Societies. |
| 1998. 5. 14. | Approved to represent Korea for the international joint research on the EMI/EMC directed by WHO. |
| 1998. 5. 14. | Technical Group on Electronic Packaging was approved. |
| 1998. 12. 16. | Technical Group on Radio Communication and Broadcasting was approved by Board of directors. |
| 1999. 5. 27. | Released the "Standards for the Emission of Electromagnetic Fields to Human Body". |
| 1999. 9. 30. | "Workshop on EMI/EMC technology and Exhibition" was held in honor of 10th Anniversary of KEES. |
| 1999. 10. 8. | Chungcheong Branch was established. |
| 1999. 11. 6. | Fifth president(Park, Dong Chul of Chungnam Univ.) was elected.(Term : 2000.1.1-2001.12.31). |
| 2000. 1. | Issuing Month of the Proceedings were changed(1, 4, 7, 10), Publication of Journals were increased to 8 times per year(two special issues were included : 1[special], 2, 4, 6, 8, 9[special], 10, 12). |
| 2000. 1. 21. | Technical group on EW was approved by Board of directors. |
| 2001. 5. | The publication of English Journal(JKEES)(twice a year : May and Nov.) was approved by Board of Directors. |
| 2001. 9. 21. | Technical group on SDR(Software Defined Radio), Optical Waves as well as Technical group on EM Education were approved by Board of Directors. |
| 2001. 11. 3. | Sixth president(Kim, Dong Il of Korea Maritime Univ.) was elected(Term : 2002.1.1- 2003.12.31). |
| 2002. 1. | The number of Journal publication became 12 times per year(two special issues and JKEES were included : 1[special], 2, 4, 5[JKEES], 6, 7, 8, 9[special], 10, 11[JKEES], 12). |
| 2002. 4. | Technical group on Radar was approved by Board of directors. |
| 2003. 1. | The publication of Korean Journal was approved by Board of Directors. The number of Journal publication became 14 times per year.(including 2 times JKEES) |
| 2003. 11. 15. | Seventh president(Seung-In Yang of Soongsil Univ.) was elected(Term : 2004.1.1- 2005.12.31). |
| 2004. 1. | The number of JKEES publication became 4 times per year. (3, 6, 9, 12) |
| 2005. 11. 5. | Eighth president(Noh-Hoon Myung of KAIST.) was elected. (Term : 2006.1.1- 2006.12.31) Chief vice president(Sang-Won Yun of Sogang Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2006.1.1- 2006.12.31) |
| 2006. 6. 8. | Technical groups merged and renamed. (Electromagnetic Environment, Electronic Materials and Components, EMI/EMC Standards were merged : EMC technology, Optical waves was renamed Thz & Optical wave technology) |
| 2009. 9. 23 | Conclude a MOU with IEICE-CS |
| 2006. 11. 3. | Nineth president(Sang-Won Yun of Sogang Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2007.1.1- 2007.12.31) Chief vice president(Young-Ki Cho of Kyungpook Nat'l Univ.) was elected. |
| 2006. 12. 20 | Spectrum Policy Special Committee was approved by Board of directors. |
| 2007. 7. 19 | Gangwon branche was established. |
| 2007. 11. 8 | English name was renamed as KIEES "The Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science" |
| 2007. 11. 30. | Tenth president(Young-Ki Cho of Kyungpook Nat'l Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2008.1.1- 2008.12.31) Chief vice president(Jeong-Ki Pack of Chungnam Nat'l Univ.) was elected. |
| 2007. 12. 7 | Jeju branche was established. |
| 2008. 1. | Began to publish the Proceeding(Electromagnetic Technology) bimonthly. |
| 2008. 11. 6. | 11th president(Jeong-Ki Pack of Chungnam Nat'l Univ.) was elected.(Term : 2009.1.1- 2009.12.31) Chief vice president(Hae-Young Lee of Ajou Univ.) was elected. |
| 2009. 2. 5 | Technical group on Electromagnetic Security was approved by Board of directors. |
| 2009. 4. 10 | Conclude a MOU with KORPA |
| 2009. 4. 28 | Conclude a MOU with KCC RRA |
| 2009. 10. 15 | Technical groups separated and renamed. (separated : Microwaves and Wave Propagation, Antennas and Propagation / renamed : Advanced RFID/USN Technology, Spectrum Management and Engineering, Electromagnetic Measurements Technology, Education Research for RFWave Engineering, CR/SDR, / established : Next Generation Broadcast Technology, Future Electromagnetic Technology) |
| 2009. 11. 5. | 12th president(Hae-Young Lee of Ajou Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2010.1.1- 2010.12.31) Chief vice president(Young-Joong Yun of Yonsei Univ.) was elected. |
| 2010. 1. 21. | Technical group on Space Environment and Radio Applications was approved by Board of directors. |
| 2010. 4. 22 | Conclude a MOU with IEEE AESS : APSAR 2011 Co-Sponsor |
| 2010. 4. 26 | Conclude a MOU with KCC CRMO |
| 2010. 10. 28. | 13th president(Young-Joong Yun of Yonsei Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2011.1.1- 2011.12.31) Chief vice president(Ki-Chai Kim of Yeungnam Univ.) was elected. |
| 2011. 11. 25. | 14th president(Ki-Chai Kim of Yeungnam Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2012.1.1- 2012.12.31) Chief vice president(Jaehoon Choi of Hanyang Univ.) was elected. |
| 2012. 11. 30. | 15th president(Jaehoon Choi of Hanyang Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2013.1.1- 2013.12.31) Chief vice president(Taek Kyung Lee of Korea Aerospace Univ.) was elected. |
| 2013. 12. 6. | 16th president(Taek Kyung Lee of Korea Aerospace Univ. ) was elected. (Term : 2014.1.1- 2014.12.31) Chief vice president(Kyung Heon Koo of Incheon National Univ.) was elected. |
| 2013. 12. 6. | Publication of the 20th anniversary of the Institute's founding book |
| 2014. 5. 1. | Re-new MOU with the National Radio Research Agency |
| 2014. 5. 8. | Conclude a MOU with the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute |
| 2014. 10. 30. | 17th president(Kyung-heon Koo of Incheon National Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2015.1.1- 2015.12.31) Chief vice president(Sang-wook Nam of Seoul Nat’l Univ.) was elected. |
| 2014. 10. 30. | Re-named the Technical group on "Electronic Packaging" to the "High-Speed Interconnect and Packaging" |
| 2014. 12. 17. | Conclude a MOU with Information & Telecommunication Technology Promotion |
| 2015. 6. 19. | Conclude a MOU with Vietnam Hanoi University of Technology |
| 2015. 10. 29. | 18th president(Sang-wook Nam of Seoul National Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2016. 1.1- 2016.12.31) Chief vice president(Cheol-heon Seo of Soongsil Univ.) was elected. |
| 2016. 4. 21. | JEES (Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science) included in SCOPUS. |
| 2016. 4. 21. | Re-named the Technical group on "Next-Generation RFID/USN" to the "Intelligent IoT Device". |
| 2016. 4. 28. | Conclude a MOU with the Air Force Headquarters. |
| 2016. 11. 27 | 19th president(Cheol-heon Seo of Soongsil Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2017. 1. 1- 2017.12.31) Chief vice president(Bomson Lee of Kyung Hee Univ.) was elected. |
| 2017. 5. 30. | Conclude a MOU with the Hanwha Systems. |
| 2017. 9. 26. | JEES included in ESCI (Emerging Sources Citation Index) |
| 2017. 11. 23. | 20th president(Bomson Lee of Kyung Hee Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2018. 1. 1- 2018.12.31) Chief vice president(Jeong-Hae Lee of Hongik Univ.) was elected. |
| 2018. 11. 22. | 21th president(Jeong-Hae Lee of Hongik Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2019. 1. 1- 2019.12.31) Chief vice president(Kyeong-Sik Min of Korea Maritime & Ocean Univ.) was elected. |
| 2018. 11. 22. | 22th president(Kyeong-Sik Min of Korea Maritime & Ocean Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2020. 1. 1- 2020.12.31) Chief vice president(Jin-seop Kang of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science) was elected. |
| 2019. 12. 30. | 30th Anniversary of the Institute's founding |
| 2020. 3. 19. | JEES included in SCIE (Science Citation Index Expanded) |
| 2020. 4. 21. | Awarded the Presidential Commendation for contributions to the development of information and communications technology in 2020. |
| 2020. 8. 20. | Conclude a MOU with 3rd Technical Headquarters ADD, LIG NEX1, KATRI, Renewal Conclude a Hanwha System. |
| 2020. 11. 20. | 23th president(Jin-Seob Kang of KRISS) was elected. (Term : 2021.1.1.- 2021.12.31) Chief vice president(Seong-Ook Park of KAIST) was elected. |
| 2021. 8. 19. | Conclude a MOU with 3rd Technical Headquarters KEIT, KOMERI, KT. |
| 2021. 11. 19. | 24th president(Seong-Ook Park of KAIST) was elected. (Term : 2022.1.1.- 2022.12.31) Chief vice president(Jong-Gwan Yook of Yonsei Univ.) was elected. |
| 2021. 12. 13. | Awarded the Minister of Science and ICT to the Excellence Institute in Academic Activities 2021. |
| 2022. 7. 5. | Conclude a MOU with the Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd |
| 2022. 11. 18. | 25th president(Jong-Gwan Yook of Yonsei Univ.) was elected. (Term : 2023.1.1.-2023.12.31) Chief vice president(Chun-sik Cho of Korea Aerospace Univ.) was elected. |
| 2022. 12. 5. | Conclude a MOU with the Ministry of National Defense, the IITP and other representative Institutes in the ICT field |
| 1. Introduction | ||||||||||||||||
| Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is an engineering field that refers to all the techniques of electronic system design to control the intensity of unwanted electromagnetic waves (Electromagnetic Interference: EMI) to be maintained within the set limit. It includes the research and development methods to minimize the electromagnetic emission impact on peripheral devices, and at the same time protecting them from peripheral devices or the environment, which is called electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS). EMC technical sub-committee group was founded when KIEES was first formed in 1989. The group specializes in researching the latest trends on protecting the environment with unwanted electromagnetic noise, developing technologies for electromagnetically compatible system designs and countermeasures for electromagnetic harm, developing new materials and electromagnetic components, and proposing international standards for EMC. |
||||||||||||||||
| 2. Prime Activities | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| 3. History | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| 4. Honorary Chairman | ||||||||||||||||
|
| EMF(Electromagnetic Field) and Biology |
| Introduction |
| Our research society focuses on studying the biological effects of electromagnetic fields. Since the early 1990s, concerns have been raised in Korea about the potential harm of electromagnetic fields on human health. As a result, many ordinary people have become interested and anxious about this issue. To approach the question of whether electromagnetic fields affect the human body empirically and academically and to inform the general public of accurate facts regarding any such effects, the Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science established the "Korea Bioelectromagnetics Research Society" in April 1996. This Society laid the foundation for conducting systematic research on the biological effects of electromagnetic fields. It comprises experts from various fields, such as engineering, medicine, biology, and physics, who work at universities, research institutes, and industries. The society has conducted studies from various perspectives to research the biological effects of electromagnetic fields in extremely low frequency and radio frequency (RF) communication bands. These include animal and cellular experiments, epidemiological survey research, analyses of RF electromagnetic wave exposure and computer numerical analysis methods, measurement and analysis of electromagnetic environment conditions in Korea, and research on standards for the protection of the human body from exposure to electromagnetic waves. Furthermore, many studies are currently underway to identify the mechanisms linking electromagnetic fields and biological effects. The members of our research society have gained international recognition over the past 20 years for their activities, including high-quality publications and participation in major conferences. Moreover, in recent years, our research society's reputation has been maintained thanks to the participation of young researchers. Our research society’s website: www.emf.or.kr |
| Major Research Areas |
| 1) Academic research on the biological effects of electromagnetic fields 2) Research on trends in domestic and international standards for electromagnetic field safety 3) Risk communication regarding the health hazards of electromagnetic fields 4) Research on medical and engineering applications of electromagnetic waves 5) Public awareness and policy-based research related to electromagnetic waves and the prevention of associated risks |
| History |
| 1996 Korea Bioelectromagnetics Research Society has been launched at KIEES 1999 1st Korea-Japan Joint EMF Workshop (Predecessor of GLORE Meeting) 2001 WHO Regional Meeting was held in Seoul 2005 WHO IAC Meeting 2010 BEMS 2010 was held in Seoul 2014 Prof. Nam Kim was elected the president of the BEMS society 2020 The KEHC (Korea EMF Health Criteria) was published 2021 25th Workshop on the Bio-Effects and Environment of EMF 2022 A book titled “Human Effects on 5G EMF” was published |
| Honorary Chairman |
| 1st (1996~2001) Prof. Yoon-Myoung Gimm 2nd (2002~2004) Prof. Jeong-Ki Pack 3rd (2005~2014) Prof. Nam Kim 4th (2015~2018) Prof. Yun-Sil Lee 5th (2019~2022) Prof. Young-Hwan Ahn |
| Electromagnetic Security | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Introduction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Given the rapid development of IT technologies based on electronic and electrical engineering, informatization and automation are required for the power and telecommunication networks, which are critical national infrastructures. Consequently, electronic and communication equipment and control systems in such facilities are interlinked. Information leakage and malfunctions caused by the high-power electromagnetic pulse emitted from these types of equipment and systems can cause large-scale damage, especially in national security installations. As such, the importance of electromagnetic security has been recognized throughout the world, and the prevention of information leakage by electromagnetic wave shielding and the protection of backbone energy and telecommunication systems from high-power electromagnetic pulse, in particular, have become preeminent issues. The aim of the Technical Group for Electromagnetic Security is to study security matters related to electromagnetic wave leakage and technologies for the prevention of damage caused by the high-power electromagnetic pulse. * Major Activities;
1) Study and exchange of technical information on the prevention of interference of high-power electromagnetic wave; |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Greetings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dear Members, The activities of the Technical Group for Electromagnetic Security are focused on security matters related with electromagnetic wave leakage and technologies for the prevention of damage caused by the high-power electromagnetic pulse, issues which are currently attracting considerable attention. We hope for your continued interest and active participation. Thank you very much. Chairperson, Jong Hwa Kwon |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Technical Group Leader / Chairperson 1st : Yeon-Choon Chung (Professor @ SeoKyeong Univ., 2009.4 ~ 2012.12) 2nd : Jae-Wook Lee (Professor @ Korea Aerospace Univ., 2013.1 ~ 2016.12) 3rd : Tae Heon Jang (Director @ Korea Test Laboratory, 2017.1 ~ 2018.12) 4th : Jong Hwa Kwon (Principal Engineer @ ETRI, 2019.1 ~ 2020.12) 5th : Gu Yeon Kim (Director @ RAPA 2021.1 ~ 2022.12) 6th : Jong Hwa Kwon (Principal Engineer @ ETRI, 2019.1 ~ Present) Principal Activities - Hosted annual Workshop on electromagnetic security - Visits to industries and holding of meetings for the exchange of study results |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. Organizational Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Chairperson: Dr. Jong Hwa Kwon (ETRI) Vice Chairperson: Dr. Han Chul Shin (RAPA) Assistant Administrator: TBD |
| Electromagnetic Wave Education | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Sub-committee for Educational Research in RF Engineering was established with the aim to advance RF engineering, electromagnetic waveapplication technology through educational initiatives and research, in 2001. We have contributed to academic and industrial development and the expansion of the accessibility and use of RF and electromagnetic wave technology through the education of personnel in the field of electromagnetic wave technology at universities, research institutes, and industries. As part of this, we have been organizing various events to help beginners and practitioners acquire professional and practical knowledge of various electromagnetic field technologies that are being utilized in industries. In the future, we will continue to develop various programs for people working in the field of electromagnetic field technology, starting with education where beginners in the field of electromagnetic field technology can learn the basics of radio waves. We also want to continuously contribute to the development of the field of electromagnetic field technology through research on the demand and supply of radio personnel and activities related to personnel development. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greetings | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dear Members and Visitors, Electromagnetic wave technology is being widely utilized in various fields, such as wireless communication, household appliances, automobiles, and manufacturing systems, including smartphones and satellite communication. As a result, the demand for education in related industries and research fields is increasing. To address this trend, we plan to develop and operate ‘various short-term education courses’ for major industries and research fields in conjunction with the ‘RF Circuit Technology Workshop’ that we have been conducting for beginners every year. In particular, we aim to develop specialized education courses that can effectively meet the demands of the related fields by continuously obtaining relevant field requirements through surveys and other means, especially for industries and research fields that have received national attention. We will make a roadmap and implement it step by step to provide information and opinion for university education that considers industrial field and technological changes, and to establish an educational environment for practical training that is highly demanded by the industry. We look forward to receiving diverse opinions and participation from you in our research activities. Thank you HarkByeong Park Chair, Technical committee for Electromagnetic Wave Education |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prime Activities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- Holding RF Circuit Technology Workshop
|
JEES
(Journal of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science)

JKIEES
The Journal of Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science

| Ikmo Park | Ajou University, Korea |
| You Chung Chung | Daegu University, Korea |
| Chang kun Park | Soongsil University, Korea |
| Byung-Jun Jang | Kookmin University |
| Chang Joo Kim | ETRI, Korea |
| Hyun Ho Park | Suwon University, Korea |
| Yong Heui Cho | Mokwon University, Korea |
| Sang Hong Park | Pukyong University, Korea |
| In-Sik Choi | Hannam Unibversity, Korea |
| Moon-Que Lee | The University of Seoul, Korea |
| Min Ho Ka | Yonsei University, Korea |
| Dong Gun Kam | Ajou University, Korea |
| Young-Houng Kang | Kunsan University, Korea |
| Il-Suek Koh | Inha University, Korea |
| Hyung Yun Kong | University of Ulsan, Korea |
| Jong-Hwa Kwon | ETRI, Korea |
| Kang Wook Kim | Kyungpook Nat'l University, Korea |
| Kyung-Tae Kim | POSTECH, Korea |
| Dong Wook Kim | Chungnam Nat'l University, Korea |
| Dong-Ho Kim | Sejong University |
| Byung Sung Kim | SungKyunkwan University, Korea |
| SoYoung Kim | SungKyunkwan University, Korea |
| Young Soo Kim | Kyung Hee University, Korea |
| Il kyu Kim | DTaQ, Korea |
| Jae Hee Kim | Koreatech Unibversity, Korea |
| Jeong Geun Kim | Kwangwoon University, Korea |
| Jung Il Kim | KERI, Korea |
| Jeong Phill Kim | Chung-Ang University, Korea |
| Jong Sung Kim | Kyungsung University, Korea |
| Ji Sung Kim | Suwon Science College University, Korea |
| Jin Gook Kim | Unist University, Korea |
| Hyeong Seok Kim | Daeyeong Ubitec., Korea |
| Wan Soo Nah | SungKyunkwan University, Korea |
| Byung Wook Min | Yonsei University, Korea |
| Duk Kyu Park | Mokwon University, Korea |
| Seong Gyoon Park | Kongju Nat'l University, Korea |
| Seung Keun Park | ETRI, Korea |
| Yong Bae Park | Ajou University, Korea |
| Ji Hoon Bae | ETRI, Korea |
| Gang Il Byun | UNIST, Korea |
| Woo jin Byun | ETRI, Korea |
| Young Je Sung | Kyonggi University, Korea |
| Seong Ho Son | Soon Chun Hyang, Korea |
| Eak Hwan Song | Kwangwoon University, Korea |
| Hyunchol Shin | Kwangwoon University, Korea |
| Seung Young Ahn | KAIST, Korea |
| Seok Honn Oh | Kbsi, Korea |
| Hyuk Jun Oh | Kwangwoon University, Korea |
| Yu Hyung- Suk | Hanyang University, Korea |
| Ick Jea Yoon | Chungnam Nat'l University, Korea |
| Byungje Lee | Kwangwoon University, Korea |
| Woo Kyung Lee | Korea Aerospace University, Korea |
| Won Cheol Lee | Soongsil University, Korea |
| Il kyu Lee | Kongju Nat'l University, Korea |
| Jae Hyun Lee | Chungnam Nat'l University, Korea |
| Haeng Seon Lee | Sogang University, Korea |
| Sungjoon Lim | Chung-Ang University, Korea |
| Chang Heon Lim | Pukyong National University |
| Sang-Geun Jeon | Korea University, Korea |
| Kyung Young Jung | Hanyang University, Korea |
| Young Bae Jung | Hanbat Nat'l University, Korea |
| Eui Rim Jeong | Hanbat Nat'l University, Korea |
| hor yung jeong | Korea Aerospace Research Institute |
| Choon Sik Cho | Korea Aerospace University, Korea |
| Eun Mi Choi | UNIST, Korea |
| Hyung-Do Choi | ETRI, Korea |
| Hosung Choo | Hongik University, Korea |
| Ki Jin Han | Dongguk University, Korea |
| Han Dong Suk | Kyungpook Nat'l University, Korea |
| Seung-Yeup Hyun | Jeju Nat'l University, Korea |
| Ic-Pyo Hong | Kongju Nat'l University, Korea |
| Seungyoung Ahn | Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Korea |
KIEES Magazine: Electromagnetic Technology

| Byung-Wook Min | Yonsei University |
| Conference | Date | Place | Organizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| The 5th Winter Conference of the KIEES | 15~28, Feb. | Jeju Haevichi Hotel & Resort | Winter Conference Committee |
| The 30th Workshop on Advanced Radio Technology | 28, April. | The K-Hotel Seoul | New Technology Ventures Committee |
| The 31st Workshop on Radio Policy | 9, June. | KBIZ, Yeouido | Policy Business Committee |
| The 2023 Summer Short Course on Radio Engineering #3 #4 | 1~4, Aug 10~11, Aug. |
Univ. of Seoul | Education Committee |
| The 11th Summer Conference of the KIEES | 23-26, Aug. | Sonofelice Del Pino, Goseong | Summer Conference Committee |
| The Workshop on Future Radio Technologies for Unmanned Vehicles | 11, Oct. | NAJU CENTUM BUSINESS HOTEL | Honam, Youngnam Branch(Joint) |
| The Workshop on Space and Defense Advanced Technologies | 13, Oct. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Space & Defense Technology Committee |
| The Conference on Radio and Wireless Communications. | 27, Oct. | Hanbat Univ. | Chungcheong Branch |
| The 35th General Meeting and the Fall Conference of the KIEES | 24, Nov. | Yonsei University Engineering Hall | Academic Research Committee |
| The Year-End Party of the KIEES | 14, Dec. | Yonsei University Baekyangnuri | General Affairs Committee |
| Workshop | Date | Place | Organizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workshop on RF Circuit Technology in 2023 (participating as a tutorial in the Winter Conference) |
15, Feb. | Jeju Haevichi Hotel & Resort | Radio Education Technical Community |
| The 15th Workshop on Electromagnetic Wave Measurement Technology | 24, March. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Electromagnetic Measurement Technology Technical Community |
| Workshop on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technologies in 2023 | 31, March. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Microwave Technical Community |
| Workshop on Antenna Technologies in 2023 | 21, April. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Antenna and Propagation Technical Community |
| Workshop on Medical Devices Using Radio Waves in 2023 | 19, May. | aT Center(Seoul) | Radio Medical Research Team |
| Workshop on Space Radio Environments in 2023 | 25, May. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Space Radio Technical Community |
| Workshop on Terahertz Technologies in 2023 | 30, June. | Construction Bldg. | THz and Optical Wave Technical Community |
| Workshop on Cognitive Radio Technologies in 2023 | 11-12, July. | Marianne Hotel, Pusan | CR/SDR Technical Community |
| EMC KOREA 2023 | 13, July. | KOFST | EMC Technical Community |
| Workshop and Short Course on Radar in 2023 | 20-21, July. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Radar Technical Community |
| Electromagnetic Wave Technology Short Course 2023 | 17-18, Aug. | TTA(Bundang) | Technical Community for Electromagnetic Wave Education |
| Workshop on Electromagnetic Field Analysis (participating as a workshop in the Summer Conference) |
23, Aug. | Sonofelice Del Pino, Goseong | Antenna and Propagation Technical Community |
| The 27th Workshop on the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields | 8, Sep. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Electromagnetics and Bio-Effects Technical Community |
| Workshop on Electronic Warfare Workshop in 2023 | 13-14, Sep. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Information Electronics Technical Community |
| High Speed Interconnect and Packaging Workshop in 2023 | 22, Sep. | aT Center (Seoul) | High Speed Interconnect and Packaging Technical Community |
| Workshop on Intelligent IoT Device Technologies | Oct. | Seoul Venture University | Intelligent IoT Device Technical Community |
| The 16th Workshop on High-Frequency Parts for Military Use | 30, Oct. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Radar Technical Community(Joint) |
| Workshop on Electromagnetic Wave Security (EMSEC) in 2023 | 9, Nov. | The K-Hotel Seoul | Electromagnetic Security Technical Community |
Those interested in participating in the activities of the Institute can submit an application form and pay the admission fee and annual membership fee according to the requirements described below.
The organization members who are interested in subscriptions to academic journal and papers can also submit an application form and pay the membership fee. After qualification review, final member admission will be given.
Those recommended by the institutes or the Institute's head of corporation can be considered for full membership.
• Those who have a university degree(4 years) or equivalent education level and more than 3 years of work experience in a relevant field
• Those who have a college degree(2 years) or equivalent education level and more than 6 years of work experience in a relevant field
Those who do not satisfy the requirements for full membership but work in a field related to the Institute can be considered for associate membership.
Student memberUndergraduate students who are majoring in a related field can be considered for student membership.
Special memberIndividuals, groups, or corporations that provide substantial financial support, giving approval to the aim of the Institute
Organization memberOrganizations, corporations, and libraries that subscribe to the periodicals published by the Institute
Fee descriptions| Annual fee | Full member | KRW 60,000 |
|---|---|---|
| Associate member (graduate student) |
KRW 40,000 | |
| Student member (undergraduate student) |
KRW 30,000 | |
| Organization member | KRW 250,000 (libraries, schools, and other organizations) |
|
| Special member | KRW 2,000,000 or more | |
| Lifetime membership fee | KRW 600,000 |
※ Fee payment can be made through an electronic billing system or transferred to the account below. You can also pay by credit card on the Institute’s homepage.
• Electronic billing number: 7638132
• IBK: 208-017491-04-010/Hongdae Station branch
• Account holder: Korean Institute of Electromagnetic Engineering and Science
※ Please write the name of payer when you make payment. Otherwise, please contact the Institute’s office after paying.
| Position | Name | Task | Contact (82-2-337-9666) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chief | Park Jeeyoun | General Affairs | Extension #5 | jyp@kiees.or.kr |
| Deputy Manager | Jeon Hye-yeong | Meetings, Winter Conference,.. | Extension #4 | happy00@kiees.or.kr |
| Manager | Park Ji-young | Projects, Proceedings, Summer Conference,.. | Extension #3 | jjung@kiees.or.kr |
| Manager | LEE Yoojin | JEES, Fall Conference, Management Technical Group & Workshops,... | Extension #2 | youzhen@kiees.or.kr |
| Assistant Manager | Jin Da-hee | Journal, Newsletter, Technical Group Workshops,... | Extension #1 | dh@kiees.or.kr |